Jido
The robot
 Jido is a MP-L655 platform from Neobotix, equipped with a Mitsubishi PA-10 arm with 6 degrees of freedom). Several sensors are available on the platform: sonar, 2 Sick laser range finders, 2 stereo camera banks (one mounted on the arm, and the other on a pan-tilt unit on the base platform).
Jido is a MP-L655 platform from Neobotix, equipped with a Mitsubishi PA-10 arm with 6 degrees of freedom). Several sensors are available on the platform: sonar, 2 Sick laser range finders, 2 stereo camera banks (one mounted on the arm, and the other on a pan-tilt unit on the base platform).
Software Architecture
The software architecture is an instance of the LAAS architecture "LAAS Architecture for Autonomous System".
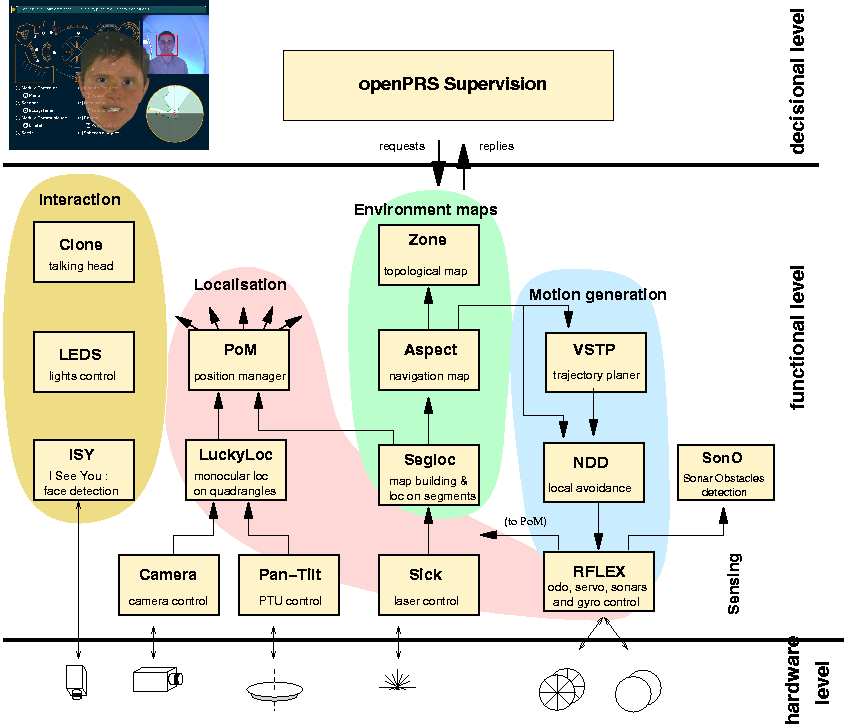
It is a hierarchical architecture including a supervisor written with openPRS (a Procedural Reasoning System) that controls a distributed set of functional modules.
Localization
 To localize itself within its environment the robot uses a SICK laser that exports at the required rate the laser echoes together with segments deduced from aligned echoes.
To localize itself within its environment the robot uses a SICK laser that exports at the required rate the laser echoes together with segments deduced from aligned echoes.
These segments are matched with segments previously recorded in a map thanks to a classical SLAM procedure.
Navigation
Jido navigation
Manipulation
Obstacle Detection
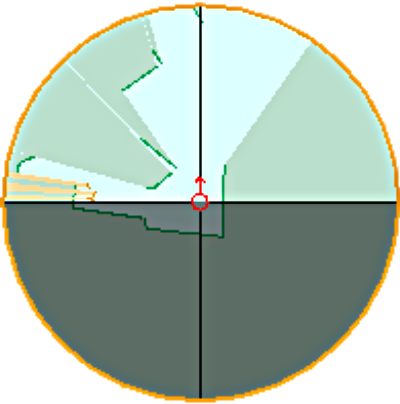 Obstacle detection is a critical function both for security reasons and for interaction purposes.The most efficient sensor is the laser. However Rackham's laser can only look forward (over 180 degrees) in an horizontal plan.
Obstacle detection is a critical function both for security reasons and for interaction purposes.The most efficient sensor is the laser. However Rackham's laser can only look forward (over 180 degrees) in an horizontal plan.
To partially overcome these limitations, the laser data are integrated in a local map and filtered using knowledge about the global map.
Human Detection
 A module is able to detect faces in real time from a color camera image.
A module is able to detect faces in real time from a color camera image.
The detector uses a cascaded classifier and a head tracker based on a particle filter.
Speech Recognition
Some wors about irit and speech recognition
Talking Head
 We use a talking head, or clone, developed by the Institut de la Communication Parlée .
We use a talking head, or clone, developed by the Institut de la Communication Parlée .
The clone is based on a very accurate articulatory 3D model of the postures of a speaking locutor with realistic synthetic rendering thanks to 3D texture projection.
Supervision
or how to make all that things work together ??